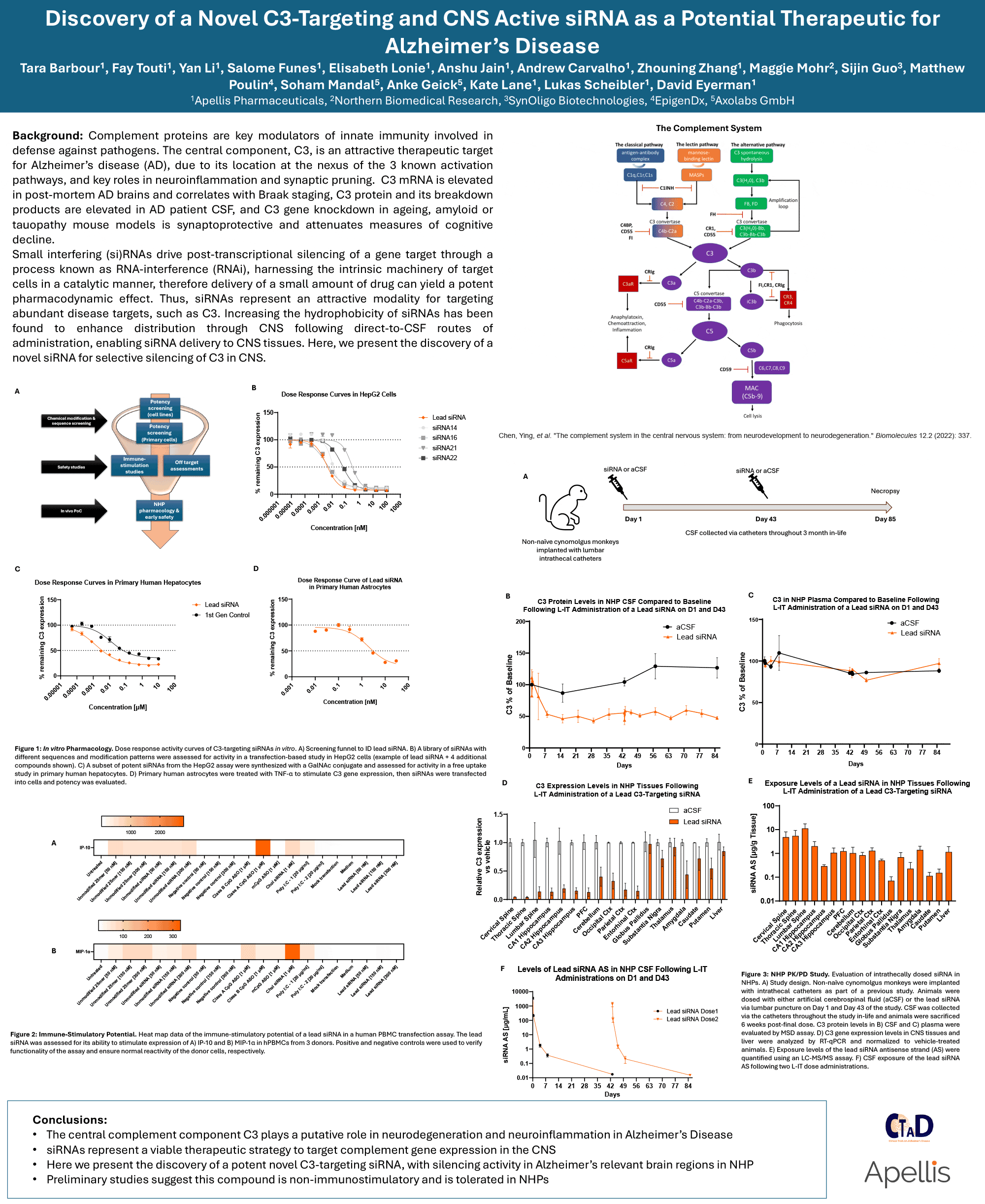
Complement component C3 plays a central role in neuroinflammation and synaptic dysfunction in Alzheimer’s disease (AD), making it a compelling therapeutic target. Here, we describe the discovery and characterization of a novel small interfering RNA (siRNA) with selective activity against C3 mRNA in central nervous system (CNS) tissues. Using a screening funnel approach, we identified a lead siRNA with high potency in human-derived cells and demonstrated its ability to silence C3 in key AD-relevant brain regions in nonhuman primates (NHPs) following intrathecal administration. The siRNA exhibited robust distribution across CNS tissues, durable C3 knockdown, and a favorable safety profile with low immunostimulatory potential. These findings support the therapeutic potential of CNS-active siRNAs targeting C3 in the treatment of neurodegenerative diseases such as AD.
Discovery of a Novel C3-Targeting and CNS Active siRNA as a Potential Therapeutic for Alzheimer’s Disease
Authors
Tara Barbour, Fay Touti, Yan Li, Salome Funes, Elisabeth Lonie, Anshu Jain, Andrew Carvalho, Zhouning Zhang, Maggie Mohr, Sole Gatto, Sijin Guo, Matthew Poulin, Soham Mandal, Anke Geick, Kate Lane, Lukas Scheibler, David Eyerman